The American Diabetes Association recommends that testing to detect pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes be considered in adults without symptoms who are overweight or obese and have one or more additional risk factors for diabetes. In those without these risk factors, testing should begin at age 45. Risk factors for…
-
-
Actos, an anti-diabetic drug prescribed for type 2 diabetes, and sometimes for pre-diabetes and (off label) for polycystic ovarian syndrome in women, has been linked again to the dangerous side effect of possibly increasing the risk of bladder cancer.
-
A patient with two fasting plasma glucose levels of 126 mg per dL (7.0 mmol per L) or greater is considered to have diabetes mellitus. Although high fasting blood glucose (blood sugars) can be an indication of type 1 diabetes (which develops over days or weeks instead of years) most…
-
Type 2 diabetes occurs when insulin-producing in your pancreas either do not make enough insulin, or, you no longer have normal sensitivity to the insulin produced by your pancreas (insulin resistance)...
-
There are many health disorders than can be associated with pre-diabetes. If you have polycystic ovarian syndrome, thyroid disease, or a family history of type 2 diabetes, you should consider being tested for pre-diabetes. If you experience unexplained rapid weight gain, you should ask your doctor about insulin resistance and…
-
Pre-diabetes is diagnosed when blood sugars are mildly elevated but not high enough to classify a person as being diabetic. But insulin resistance can still be present even when blood sugars are still normal. People with untreated insulin resistance are at significant risk for pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Lab…
-
When a person is insulin resistant, their cells do not respond to a normal secretion of insulin from the pancreas. The pancreas has to work harder and make more insulin than normal than normal to move blood glucose (sugar) out of the blood stream and into cells and tissues.
-
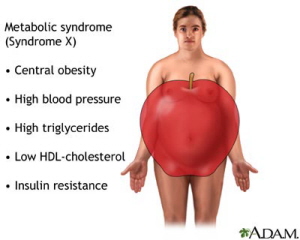
Insulin Resistance Syndrome (IRS) is also referred to as Metabolic Syndrome, or Metabolic Syndrome X and was previously simply called Syndrome X. Pre-diabetics may also have Metabolic Syndrome X, but pre-diabetes is a separate condition from metabolic syndrome.
-
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) is a term to describe when a person has elevated blood sugar (blood glucose) in response to eating. IGT is diagnosed when blood sugar levels are not normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. IGT is one reason why a person may be…
-
People with insulin resistance may have different signs and symptoms. Physical symptoms can include skin tags, acanthosis nigricans, weight gain, and hirsutism. Other symptoms can be measured in lab tests including glucose tolerance tests and fasting insulin tests...
-
Yes! A person who is insulin resistance can, and often does, have normal fasting blood glucose levels and normal blood sugar after meals. People with insulin resistance can even "pass" an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
-
The American Diabetes Association and National Institutes of Health use the term "pre-diabetes." However, either is considered correct and interchangeable. No matter what you call it, pre-diabetes is a serious metabolic condition ...
-
Are BMI Charts accurate for determining of someone is overweight? Many doctors still use this somewhat ineffective method of determining whether or not a person is over weight...
-
Information about pre-diabetes and insulin resistance: FAQs, signs and symptoms, risk factors, what it is, how pre-diabetes is diagnosed, and how to treat it.
-
A person who is insulin resistant usually produces higher levels of insulin from the pancreas than is normal or healthy. Over production of insulin (hyperinsulinemia) can aggravate or trigger other health problems including infertility, weight gain, bloating, poor lipid profiles, and hormonal imbalances. Hyperinsulinemia also increases the risk of more…
-
Pre-diabetes is metabolic condition that is diagnosed when a person has either Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG), or Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT). There are two blood tests that are generally used to diagnose or confirm pre-diabetes. Both of these tests are usually done in the laboratory and involve drinking a sugary…
-
How is insulin resistance diagnosed? What tests can tell me if I have insulin resistance? I have normal blood sugars, can I still have be insulin resistant? These and other questions answered about insulin resistance...
-
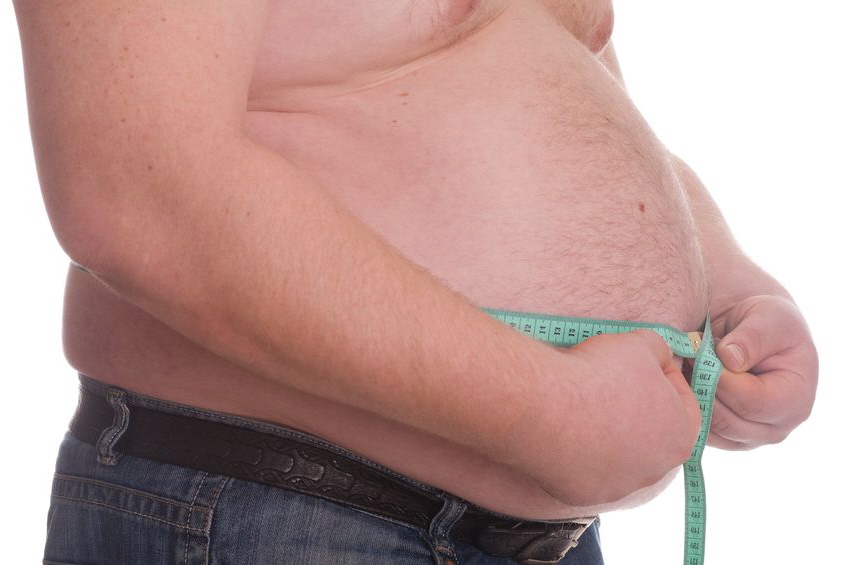
Waist-to-hip (sometimes mistakenly referred to as hip-to-waist) ratio is a comparison between your waist and your hip measurements. It does not tell you if you have pre-diabetes but can be useful in determining risk factors. According to research scientists at the Imperial College Long, the German Institute of Human Nutrition,…
-
FAQs links to information about Insulin Resistance, Syndrome X, and Pre-Diabetes. Risk factors, causes, tests, signs and symptoms, treatment, and more...
-
Links to information about Insulin Resistance Information and Frequently Asked Questions
-
Learn the difference between a disease and a syndrome and find out how pre-diabetes is classified. Pre-diabetes is a metabolic disorder. It is not considered a disease or a syndrome. However, pre-diabetes can be part of Metabolic Syndrome X (also called Insulin Resistance Syndrome), which, as is suggested by the…