A • B • C • D • E • F • G • H • I • J • K
L • M • N • O • P • Q • R • S • T
U • V • W • X • Y • Z
Medical Tests
Definitions
Background Retinopathy: A type of damage to the retina of the eye marked by bleeding, fluid accumulation, and abnormal dilation of the blood vessels. Background retinopathy is an early stage of diabetic retinopathy. Also called simple or nonproliferative (non-pro-LIF-er-uh-tiv) retinopathy.
Basal Rate: A steady trickle of low levels of longer-acting insulin, such as that used in insulin pumps.
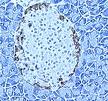
Beta Cell: A cell that makes insulin. Beta cells are located in the islets of the pancreas and are also called beta islet cells.
Blood Glucose: Â The main sugar found in the blood and the body’s main source of energy. Also called “blood sugar.”
Blood Glucose Level: The amount of glucose in a given amount of blood. Â It is noted in milligrams in a deciliter, or mg/dL.
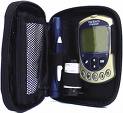
Blood Glucose Meter: Also called blood glucose monitoring kit.
A small, portable machine used by people with diabetes to check their blood glucose levels. After pricking the skin with a lancet, one places a drop of blood on a test strip in the machine. The meter (or monitor) soon displays the blood glucose level as a number on the meter’s digital display.
There are many types of blood glucose meters you can buy to check your blood glucose at home. On average, meters cost $15 to $150 dollars per kit.

Blood Glucose Monitoring: Checking blood glucose level on a regular basis in order to manage diabetes. A blood glucose meter (or blood glucose test strips that change color when touched by a blood sample) is needed for frequent blood glucose monitoring.
People with pre-diabetes generally do not need to test their blood sugar very often. But it is a good idea to check your fasting morning blood sugars from time to time to make sure your condition is not getting worse, or to detect type 2 diabetes as early as possible.



