A • B • C • D • E • F • G • H • I • J • K
L • M • N • O • P • Q • R • S • T
U • V • W • X • Y • Z
Medical Tests
Definitions
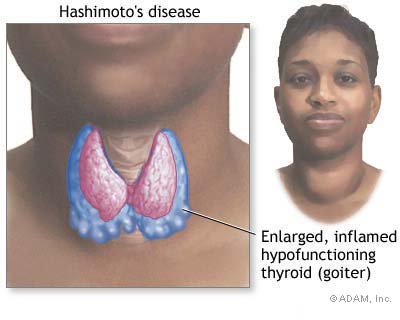
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune disorder in which the autoimmune system attacks and destroys the thyroid.  A normal TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) test may not be sufficient to rule out Hashimoto’s. Have your doctor test for specific antibodies.  A person may test positive for Hashimoto’s antibodies long before symptoms present.  People with diabetes, and women with PCOS should be tested for Hashimoto’s.
If you have Hashimoto’s you should be screened for pre-diabetes.
HbA1c Test: A test that measures a person’s average blood glucose (blood sugar) level over the previous 2 to 3 months. The most accurate clinical name for this test is the HbA1c. Also called A1c test and Hemoglobin A1c test.
HDL cholesterol (High-Density-Lipoprotein): A fat found in the blood that takes extra cholesterol from the blood to the liver for removal. Â Also called “good” cholesterol.
HDL cholesterol (High-Density-Lipoprotein) Test: HDL is a fat found in the blood. Â It is sometimes called the “good” cholesterol. HDL takes extra cholesterol from the blood to the liver for removal. Â The HDL test checks the level of HDL which is then compared to the LDL and total cholesterol.
Hemochromatosis: A disease which causes the body to store excessive amounts of iron. Hemochromatosis can cause onset of secondary type 1 diabetes.
Hemodialysis: The use of a machine to clean wastes from the blood after the kidneys have failed. The blood travels through tubes to a dialyzer, a machine that removes wastes and extra fluid. The cleaned blood then goes back into the body.
Hemoglobin A1c Test: A test that measures a person’s average blood glucose level over the past 2 to 3 months. The most accurate clinical name for this test is the HbA1c.
Hemoglobin is the part of a red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells and sometimes joins with the glucose in the bloodstream. Also called hemoglobin A1C or glycosylated (gly-KOH-sih-lay-ted) hemoglobin, the test shows the amount of glucose that sticks to the red blood cell, which is proportional to the amount of glucose in the blood. Â Also called A1c test, Glycosylated HbA1c, and Hemoglobin A1c test.
Doctors use the A1c test to see how well a patient is managing their blood sugars over a several month period of time. Â The higher a patient’s A1c, the greater their risk for developing diabetes complications.
Heredity: The passing of a trait from parent to child.
High blood sugar: See hyperglycemia.
High Blood Pressure: See hypertension.
High-Density-Lipoprotein: See “HDL.”
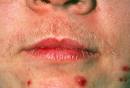
Hirsute(ism): Hairy; having excess hair on the body and/or face. Â Woman with insulin resistance, diabetes, or polycystic ovarian syndrome may develop excessive body and facial hair (often in a male pattern).
Honeymoon Phase: Temporary remission of hyperglycemia that occurs in some people newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, when some insulin secretion resumes for a short time, usually a few months, before stopping again.
Hormone: A chemical produced in one part of the body and released into the blood to trigger or regulate particular functions of the body. For example, insulin is a hormone made in the pancreas that tells other cells when to use glucose for energy. Synthetic hormones, made for use as medicines, can be the same or different from those made in the body.
Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA): Proteins located on the surface of the cell that help the immune system identify the cell either as one belonging to the body or as one from outside the body. Some patterns of these proteins may mean increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Hyperglycemia: Excessive blood glucose (high blood sugar). Fasting hyperglycemia is blood glucose above a desirable level after a person has fasted for at least 8 hours. Postprandial hyperglycemia is blood glucose above a desirable level 1 to 2 hours after a person has eaten.
Hyperinsulinemia: High levels of insulin. A condition in which the level of insulin in the blood is higher than normal. Hyperinsulinemia is caused by overproduction of insulin by the body, and is usually related to insulin resistance but can also be caused by other severe medical conditions.
Hyperlipidemia: Higher than normal fat and cholesterol levels in the blood.
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS): An emergency condition in which a person’s blood glucose level is very high and ketones are not present in the blood or urine. If HHNS is not treated, it can lead to coma or death.
Hypertension: High blood pressure. A condition present when blood flows through the blood vessels with a force greater than normal. Also called high blood pressure. Hypertension can strain the heart, damage blood vessels, and increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney problems, and death.
Hypertriglyceridemia: High triglyceride levels. Triglycerides are the most common form of fat stored in the body. High triglyceride (hypertriglyceridemia) levels may occur when diabetes is out of control. High levels of triglycerides are associated with an increase risk of heart disease.
Body fat is almost entirely made up of triglycerides, and fats are mostly transported in the blood in this form as well. Triglycerides can come directly from dietary fat , or from fat converted from carbohydrates. This is one reason why people who follow low carb diets (and eat mostly protein) rarely have triglycerides above normal (150 mg/dL). This is one of the most reliable results of following a low carb way of eating.
Hypoglycemia: A condition that occurs when one’s blood glucose is lower than normal, usually less than 70 mg/dL. Signs include hunger, nervousness, shakiness, perspiration, dizziness or light-headedness, sleepiness, and confusion. If left untreated, hypoglycemia may lead to unconsciousness. Hypoglycemia is treated by consuming a carbohydrate-rich food such as a glucose tablet or juice. It may also be treated with an injection of glucagon if the person is unconscious or unable to swallow. Also called an insulin reaction or insulin shock.
Hypoglycemia Unawareness: A state in which a person does not feel or recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). People who have frequent episodes of hypoglycemia will lose their sensitivity and may no longer experience the warning signs low blood sugar like sweating and feeling dizzy or shaky.
Hypotension: Low blood pressure or a sudden drop in blood pressure. Hypotension may occur when a person rises quickly from a sitting or reclining position, causing dizziness or fainting.



