A • B • C • D • E • F • G • H • I • J • K
L • M • N • O • P • Q • R • S • T
U • V • W • X • Y • Z
Medical Tests
Definitions
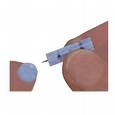

Lancet: A lancet is a small, disposable needle used to draw blood from the finger tip. Most people with diabetes use a lancing device but most doctor’s office use the one-use disposable lancets to draw blood from finger tips. [Tips on Using Lancing Devices]
Lancing Device: A spring-loaded device used to prick the skin with a small needle to obtain a drop of blood for blood glucose monitoring. The lancet inside the device should be changed every day, but does not have to be changed every time blood is drawn.
Laser Surgery Treatment: A type of therapy that uses a strong beam of light to treat a damaged area. The beam of light is called a laser. A laser is sometimes used to seal blood vessels in the eye of a person with diabetes. See photocoagulation.
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA): A condition in which type 1 diabetes slowly develops in adults. Sometimes also called type 1.5 and often misdiagnosed as type 2 diabetes in the early stages of LADA.
LDL cholesterol (Low-density Lipoprotein): A fat found in the blood, takes cholesterol around the body to where it is needed for cell repair and also deposits it on the inside of artery walls. Also called “bad” cholesterol.
Lente Insulin (L Insulin): An intermediate-acting insulin. On average, lente insulin starts to lower blood glucose levels within 1 to 2 hours after injection. It has its strongest effect 8 to 12 hours after injection but keeps working for 18 to 24 hours after injection. Also called L insulin.
Limited Joint Mobility: A condition in which the joints swell and the skin of the hand becomes thick, tight, and waxy, making the joints less able to move. It may affect the fingers and arms as well as other joints in the body.
Lipid: A term for fat in the body. Lipids can be broken down by the body and used for energy.
Lipid Profile: A blood test that measures total cholesterol, triglycerides, and HDL cholesterol. LDL cholesterol is then calculated from the results. A lipid profile is one measure of a person’s risk of cardiovascular disease.
Lipoatrophy: Loss of fat under the skin resulting in small dents. Lipoatrophy may be caused by repeated injections of insulin in the same spot.
Lipodystrophy: Defect in the breaking down or building up of fat below the surface of the skin, resulting in lumps or small dents in the skin surface. (See lipohypertrophy or lipoatrophy.) Lipodystrophy may be caused by repeated injections of insulin in the same spot.
Lispro Insulin: A rapid-acting insulin. On average, lispro insulin starts to lower blood glucose within 5 minutes after injection. It has its strongest effect 30 minutes to 1 hour after injection but keeps working for 3 hours after injection.
Liver: An organ in the body that changes food into energy, removes alcohol and poisons from the blood, and makes bile, a substance that breaks down fats and helps rid the body of wastes.
Long-Acting Insulin: A type of insulin that starts to lower blood glucose within 4 to 6 hours after injection and has its strongest effect 10 to 18 hours after injection. See ultralente insulin.
Low Blood Sugar: See hypoglycemia.
Low Carb Diet: From a purely medical standpoint, a low carb diet is the same thing as a ketogenic diet. Low carb diets consist of consuming 40 or fewer carbohydrates per day so that the dieter enters into a state of benign dietary ketosis. Many popular diets that are referred to as low carb diets are really carbohydrate modified (or reduced carbohydrate) diets and not technical “low carb” based on the medical definition.



