Table of Contents
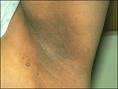
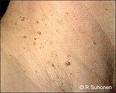
Acanthosis Nigricans: Acanthosis nigricans (AN) is typically characterized by hyperpigmentation (darkening of skin pigment) and usually accompanied by a velvety change in texture of the skin that is affected. Read more about acanthosis nigricans
Euglycemia: Normal amounts of blood sugar in the blood stream. Read more about euglycemia.
Related article: Normal, Pre-Diabetic, and Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges.
Glucose Challenge Test: A glucose challenge test measures the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood stream after the woman is “challenged” with a glucose solution. Read more about the glucose challenge test
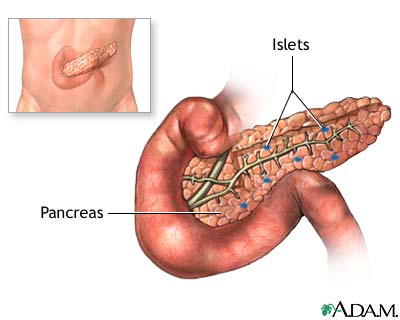
Insulin: Insulin is a hormone produced in the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin acts like a key to “unlock” cells so that blood sugar can enter into cells and tissues to nourish the body. Read more about insulin
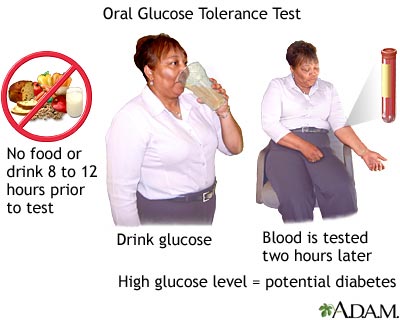
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (2-hour): To check for pre-diabetes, and see how a person reacts to a glucose load, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) may be given to check blood sugar levels 2 hours after being given 75 grams of glucose to drink.
Read more about the oral glucose tolerance test and normal and abnormal blood sugar ranges.
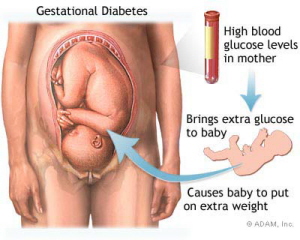
Gestational Diabetes and the OGTT For Pregnant Women
Skin Tags: A skin tag is a benign (non-cancerous) skin growth that can occur on the body or face. They can be are smooth or wrinkled, skin-colored or just slightly darker than skin color, and vary in size and can grow as large as a big grape. Read more about skin tags
Pancreas: The pancreas is an organ located behind the lower part of the stomach. It is about five inches long and approximately the size of a hand. The pancreas makes insulin and digestive enzymes that help the body use food. Read more about the pancreas
Reference Charts and Tables
- Body mass index (BMI) information
- Morning fasting blood glucose
- Oral glucose tolerance test ranges (non-pregnant)
- Oral glucose tolerance test (pregnancy)
- Glucose challenge test (screening for gestational diabetes)
- Waist-to-hip ratio chart and instructions

Changes in your lifestyle can help you reverse pre-diabetes. Learn to eat healthier, get more exercise, manage your stress levels, and see your doctor regularly.
Losing a modest amount of weight – even as little as 10-15 lbs. can help you reverse pre-diabetes.
Increasing muscle mass through strength training can help you burn fat more efficiently and make your body more sensitive to insulin.