 What is an oral glucose tolerance test for pregnant women?
What is an oral glucose tolerance test for pregnant women?
An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is usually done between the second and third trimester of pregnancy when the greatest amount of insulin resistance occurs. This test measures blood glucose (sugar)Â levels four or five times over a three-hour period. Prior to the test, the woman must not eat or drink anything but water for the previous eight to ten hours.
How an OGTT is Administered
Before starting the test, a blood sample is taken to provide a fasting glucose level. The woman then drinks about 100 grams of glucose (a sugary beverage) and blood samples are taken every hour for three hours. Some doctors only use a 2-hour glucose test (in this case only 75 grams of glucose is given to the women.)
American Diabetes Association Guidelines for
Diagnosing Gestational Diabetes via
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test During Pregnancy
| Time after glucose load (after drinking 100 grams of glucose) | Normal Ranges(1) |
| Fasting (before glucose load) | 95 mg/dL (5.3 mmol/L) or lower |
| 1 Hour after glucose load | 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) or lower |
| 2 hours after glucose load | 155 mg/dL (8.6 mmol/L) or lower |
| 3 hours after glucose load | 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) or lower |
(1) If two or more tests show blood glucose higher than the normal
ranges above, gestational diabetes will be diagnosed.
(2) A 75-gram glucose load may be used but may not be as reliable as the 100-gram glucose test.
If your doctor has you take the 75-gram test, you will not have blood drawn at the 3-hour mark.
 Why are women given an oral glucose tolerance test during pregnancy?
Why are women given an oral glucose tolerance test during pregnancy?
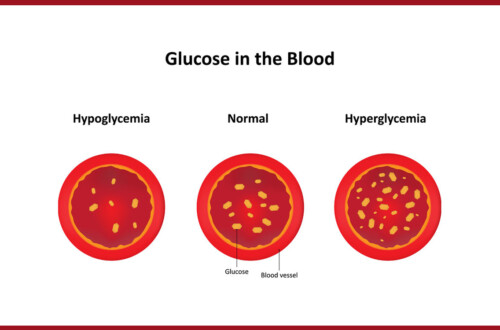
Most doctors routinely screen women for gestational diabetes because all women who become pregnant are at risk for developing gestational diabetes. If a woman has gestational diabetes she will have elevated blood sugar (blood glucose). This can cause the baby to gain too much weight and may cause health problems for the mother.
Gestational diabetes can sometimes be treated with changes in lifestyle but many women will need to take insulin during her pregnancy. In most cases, gestational diabetes resolves by itself after the baby is born. Some women remain diabetic after pregnancy and will then classified as having type 2 diabetes.